Varicose veins (VV) are a fairly common condition that affects both men and women. It affects the human lower extremities as well as the deep veins, leading to the development of thrombosis and post-thrombotic phlebitis.
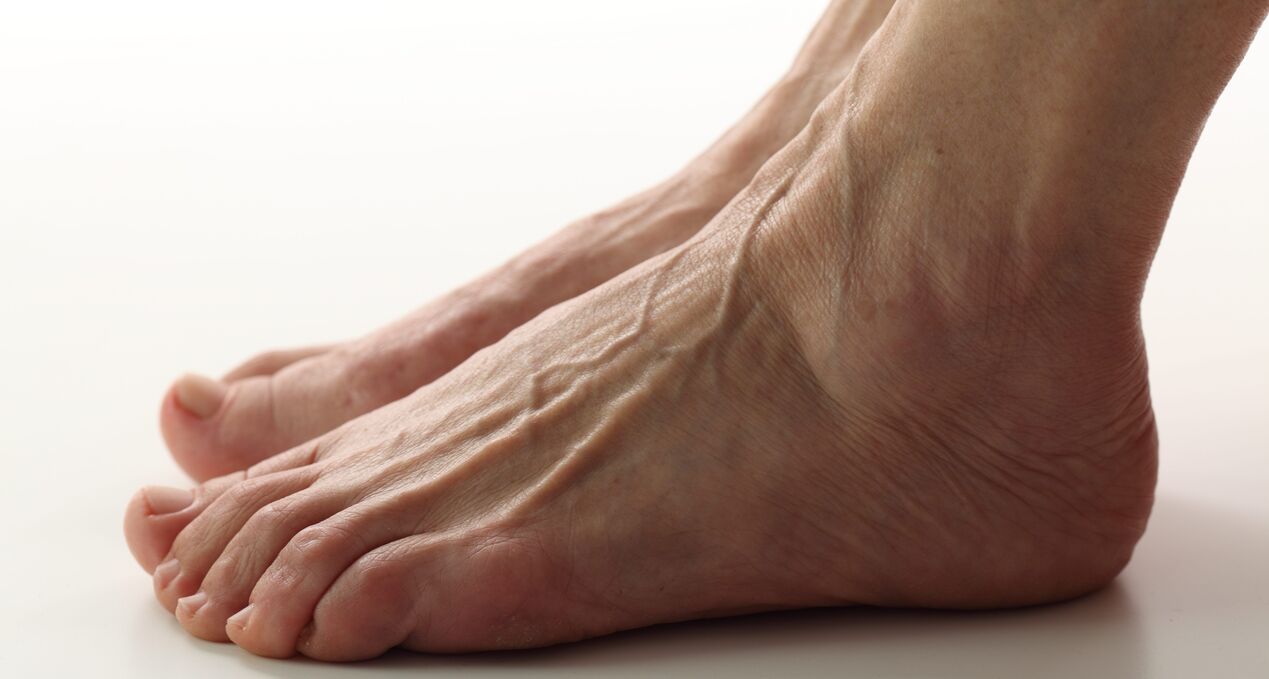
Spider veins that appear in a person's legs as the disease progresses make him begin to feel unattractive. In addition to the external, there are also internal manifestations of explosives, which manifest as discomfort and pain in the calf muscles of the legs. The development of the disease increases the risk of other diseases of the circulatory system.
The key to success in combating pathology lies in timely diagnosis and effective treatment. A big mistake one makes is to use various ointments and creams independently, which in most cases will not bring the desired results. As a result, time that could be used for correct and effective treatment is wasted.
In order to get rid of varicose veins, you need to tackle the following tasks:
- Eliminate symptoms.
- Remove varicose veins.
- Prevention of the development and recurrence of VV.
Only highly qualified specialists with sufficient experience in the treatment and prevention of such diseases can successfully tackle each of the above tasks.
Symptoms of varicose veins
The symptoms of the disease are clear signs of its development. They are divided into:
- subjective:
- Non-severe and painful pain in the calf muscles.
- There is burning and itching in the veins affected by varicose veins.
- Legs are heavy and worse by the end of the day.
- Hyperpigmentation of the skin.
- Increased lower extremity fatigue.
- Nutritional venous ulcer of the leg.
- Calf muscle pain that worsens when walking.
- Edema in the legs and feet.
- objective:
- Varicose veins, which are clearly visible even without the use of special equipment.
- Dilated intradermal and saphenous veins are seen.
- The presence of spider veins.
- Changes in skin structure and color, appearance of lipocutaneous sclerosis and venotrophic ulcers.
What do veins look like?
The first warning sign of a problem with your veins is swelling in your lower extremities at the end of the day. Puffiness is especially noticeable if a person is standing most of the day. It can go away in the morning after a night of relaxation.
However, if you don't pay attention to the problem, the situation can get significantly worse. The intradermal veins on the legs with varicose veins turn dark blue and protrude above the skin surface of the legs and feet. On the surface, they look like clusters of red grapes that are already overripe. External manifestations of this pathology are accompanied by pain in the calf, heat in the legs, swelling and cramping of the calf muscles. These symptoms are accompanied by changes in the appearance of the skin over time.
Causes of varicose veins in the lower extremities
Lower extremity VV can develop under the influence of a variety of factors and circumstances, including:
- Pregnant. This is a key risk factor for the onset of the disease. This explains the fact that women have several times more varicose veins than men. In this case, the disease develops under the influence of increased circulating blood volume and uterine compression of retroperitoneal venous pregnancy.
- obesity. Numerous studies have demonstrated a link between this condition and the development of VV. At the same time, a direct relationship was found between weight gain and an increased risk of pathological development.
- A lifestyle characterized by prolonged static loads, regular weight lifting or prolonged immobility in standing or sitting positions.
- state of discord. Their role in disease development has increased significantly in recent years. This is due to the widespread use of hormonal contraceptives, osteoporosis and premenopausal hormone replacement therapy.
- hereditary. The role of this factor in the development of leg varicose veins is not clearly established today.
- A valve device that violates the veins, causing blood flow to surge under the influence of gravity every time a person stands up. When you walk, the muscles around the deep veins contract. These veins drain, increasing venous pressure. Blood enters the superficial veins through poorly valved communicating vessels. As a result, they fill with blood, which causes them to stretch and dilate (varicose veins).
Categories and Stages
As with any disease, VV has several stages that differ from each other in terms of pathology and degree of spread of symptoms. These include the following stages:
- Initial (or compensated).
- The second (or subcompensation).
- Third (or decompensated).
It is worth noting that complications can occur in any of the above stages, but their greatest likelihood is in the latter two stages. VV can promote the development of the following diseases:
- Thrombophlebitis.
- erysipelas.
- Deep vein thrombosis.
- Nutritional eczema.
Visiting a specialist at the first signs of an attack will help reduce the risk of worsening the condition and begin removing varicose veins. Do not ignore even mild symptoms as this can lead to undesirable and extremely negative consequences.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of varicose veins, the symptoms of which are described above, provides solutions for the following tasks:
- Determine the presence or absence of pathology in each patient. Often, people without varicose veins definitely do, and vice versa. However, only an experienced phlebologist, based on external examinations and numerous complex studies, can make an accurate diagnosis.
- Establish venous pathological type characteristics. Physicians determine exactly which veins have pathological changes, the extent of such changes, and the consequences that may or have occurred.
- Prescribe the correct treatment plan. Based on the diagnosis and characteristics of each particular organism, the attending physician makes choices that favor one or another treatment or set of treatments.
- Evaluation of the level of treatment effectiveness, performed by the attending physician during resolution of the disease or after the patient has fully recovered.
The main methods of diagnosing VV include:
- Plethysmography.
- Thermal Imaging.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Ultrasound vascular scan.
- CT examination.
- Clinical study: talking to the patient, his external examination and hand examination.
- Radionuclide venography.
- Intravascular ultrasound.
- X-ray venography.
In most cases, a clinical examination and an ultrasound angiography by a specialist to diagnose leg varicose veins is sufficient.
treatment method
Modern methods of treating varicose veins are designed to reduce the degree of disability and trauma, which helps patients recover faster. The main treatments include:
- Sclerotherapy. This method involves introducing a special drug into the lumen of the varicose veins in the leg, which causes chemical burns to the walls of the internal veins. This causes them to stick and stop the pathological blood flow through them. It can be used alone or in combination with other operations. It is performed without pre-anesthesia, using a fine needle puncture through the skin. Duration depends on the extent of the lesion.
- Foam sclerotherapy involves the preparation of foam by a specialist with a special drug that works on an impressive area of the lining of the affected vein. It is used to treat large diameter veins.
- Intravenous laser coagulation, which is performed on the main trunk of the leg vein using a laser device, allows you to block the pathological blood flow through the affected vein due to burns of its inner wall and subsequent bonding.
- Veneectomy, designed to remove enlarged subcutaneous lymph nodes and tributaries due to varicose veins through skin puncture. It has excellent cosmetic benefits and can be used alone or in combination with other treatments under local anesthesia.
- Elimination of dysfunctional perforating veins for the prevention of venous insufficiency and the treatment of nutritional disorders including ulcers.
- Combined phlebectomy is a combination of several IV treatments, depending on the indication and nature of the venous pathology.
Complications of varicose veins
It should be understood that improper treatment of the disease or complete rejection of it can lead to complications. The latter appears not only in cosmetic defects of the lower extremities, but also in more serious forms. in:
- Nutritional eczema, which subsequently turns into ulcers.
- Thrombotic lesions of the venous system, including superficial vein thrombophlebitis and lower extremity deep vein thrombosis.
Venous blood is a kind of "sewers" of human tissue, rich in substances and cellular metabolites that are relatively harmful to the human body. Cells in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, as well as muscles and bones, dump tissue respiration products and other waste products into the venous system, where they are transported to the heart, lungs, kidneys, and liver. In cases of violation of the function of the venous system, the content of these products in body tissues increases.
Varicose veins Enlarged veins can lead not only to increased concentrations of harmful products in the tissue, but also to increased tissue swelling. This violation of the outflow of harmful products, combined with the swelling observed over a long period of time, leads to cell death of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, which is subsequently replaced by venous eczema, which appears as a dark dense punctate structure. The death of the superficial layer of the skin is the cause of trophic ulcers.
prevention
Varicose veins in the legs can be avoided if preventive measures are taken, and are treated today through a variety of methods. Because women are at a much higher risk of VV, they don't have to neglect prevention of the disease. However, men should also not ignore preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of varicose veins in the legs. Key activities include:
- Use topical preparations (gels, ointments, creams) that help strengthen vessel walls, optimize valve function, reduce the risk of blood clots, reduce edema, and heal wounds.
- Use compression stockings, tights, stockings, and elastic bandages. This is a great tool for fighting varicose veins. These products can be purchased in specialized stores after consulting a doctor, which is necessary because it is relatively difficult to independently determine the type of compression underwear required.
- Do special exercises every day. They were even able to stop the dilation of blood vessels that had already begun. It should be noted that if you have a BB tendency, it will make you give up heavy physical exertion, but don't ignore an active lifestyle. For example, light jogging, swimming, yoga, and skiing can help keep leg veins healthy.
- Varicose vein prophylaxis is considered a more effective method of preventing VV than the use of topical medications. However, the use of any oral medication should only be used for its intended purpose and under the strict supervision of a competent specialist.
In order to prevent the disease from getting worse, you should give up self-medication at the beginning of the disease and seek medical attention. This will make it possible to make the correct diagnosis in time and prescribe appropriate treatment to stop the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of developing other diseases to zero.
Frequently Asked Questions
Many times, people are not only interested in the question of how to treat varicose veins. Many patients with this condition are interested in what they can and cannot do so as not to aggravate their condition and cause other health problems. The following are frequently asked questions of interest to patients with VV.
Can varicose veins be vaccinated against coronavirus?
The answer to the question of whether to allow the use of the coronavirus vaccine to treat varicose veins is possible. In the absence of exacerbation, this pathology is not a limitation for COVID-19 vaccination. If a person does not have acute thrombophlebitis, then this refers to decompensation of varicose veins in the legs and does not prohibit him from being vaccinated against coronavirus infection.
Can varicose veins drink coffee?
Caffeine has the ability to increase blood pressure and increase the heartbeat, which can be detrimental to fragile, swollen veins damaged by varicose veins. Coffee has the following effects on blood vessels:
- Increased load on the vein wall.
- High blood pressure.
- Short-term venous dilation.
Therefore, people with varicose veins can drink coffee, but not more than the daily intake. Totally rejecting your favorite tonic drink won't cause diseased veins to heal, so you shouldn't torture yourself for not drinking coffee. Just don't drink more than 1-2 cups a day. It is also recommended to dilute the coffee with milk.
Can I have a massage?
Complex treatment for early varicose veins includes massage. However, it needs to be done correctly.
For varicose veins, you can do a very light massage to the lower extremities. It is also suitable for patients with simple varicose veins.
Professional manual massage is recommended for patients with varicose veins, but all features of the course of the disease must be taken into account. It is advisable to consult a specialist before massaging the area affected by varicose veins.
Can you warm your feet?
When the legs are heated, the veins dilate, blood circulation increases, and the load on the non-venous walls only increases. This can exacerbate an already poor condition for varicose blood vessels. This is why it is recommended to limit hot baths for people with varicose veins. It is best to lower the temperature of the water from hot to warm so that it does not cause vasodilation and does not worsen the condition of the body. It should always be remembered that whether we are talking about a hot bath or vaccination for varicose veins, it is necessary to consult a specialist.
Are running and squats allowed?
Experts recommend jogging at the first signs of BB development. It is important to ensure that these exercises are systematic. When running, the blood is filled with oxygen. Therefore, it is best to prioritize jogging in a forest or park with fresh air.
However, you should fully assess your abilities and endurance and avoid overloading that is contraindicated in varicose veins. It is important to monitor a gradual increase in load that does not exceed the physical comfort index.
People with BB should not get tired during a run. Only short runs with compression stockings are allowed. In the case of thrombophlebitis, jogging should be abandoned. The acceptability of running and squats for small pelvic varicose veins should be discussed with your doctor.
What is the best treatment for varicose veins?
Today, there is no clear answer to the question of which treatments are most effective for varicose veins. The truth is that the success of treatment depends on many factors that must be assessed by a qualified specialist in each case. Only after this can they make a final decision on specifying a specific treatment for the BB.
In order to prevent the disease from getting worse, you should give up self-medication at the beginning of the disease and seek medical attention. This will make it possible to make the correct diagnosis in time and prescribe appropriate treatment to stop the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of developing other diseases to zero.


















